Welcome, ERP enthusiasts! Are you gearing up for a successful ERP go-live? Implementing an ERP system can be a daunting task, but with the right checklist and preparation, you can ensure a smooth transition. From data migration to user training, there are essential steps that need to be taken to guarantee a successful ERP go-live. In this article, we will walk you through the crucial steps to include in your checklist for a successful ERP implementation.
Pre-Implementation Planning
Before diving into the actual implementation process of an ERP system, it is crucial to have a solid pre-implementation plan in place. This phase sets the tone for the entire project and can greatly influence its success. Here are some key steps to consider during the pre-implementation planning phase:
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives: The first and most important step in the pre-implementation planning process is to clearly define your goals and objectives for the ERP system. What are you hoping to achieve by implementing this new system? Are you looking to streamline your business processes, improve efficiency, or enhance your reporting capabilities? By clearly outlining your goals, you can ensure that the ERP system is designed and configured to meet your specific needs.
2. Conduct a Business Process Review: Before implementing an ERP system, it is essential to review and document your current business processes. This will help you identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. By understanding how your business currently operates, you can better align the ERP system with your needs and ensure a smooth transition.
3. Establish a Project Team: Implementing an ERP system is a complex and multifaceted project that requires input from various departments within your organization. It is important to establish a project team consisting of key stakeholders, subject matter experts, and IT professionals. This team will be responsible for overseeing the implementation process, making decisions, and ensuring that the project stays on track.
4. Develop a Budget and Timeline: Implementing an ERP system is a significant investment that requires careful planning and budgeting. It is important to develop a realistic budget that takes into account the costs of software licensing, hardware, implementation services, training, and ongoing support. In addition, you should establish a timeline for the implementation project, taking into consideration factors such as resource availability, dependencies, and potential obstacles.
5. Assess and Select an ERP System: Once you have defined your goals, reviewed your business processes, established a project team, and developed a budget and timeline, it is time to assess and select an ERP system. This process involves evaluating different ERP vendors, conducting demonstrations and trials, and ultimately selecting the system that best meets your needs. It is important to involve key stakeholders in this process to ensure that the chosen system aligns with your goals and objectives.
By following these key steps during the pre-implementation planning phase, you can set your ERP implementation project up for success. By clearly defining your goals, reviewing your business processes, establishing a project team, developing a budget and timeline, and selecting the right ERP system, you can ensure a smooth and successful implementation process.
Data Migration Strategy
When it comes to implementing a new ERP system, data migration is a crucial step that can often be overlooked. Having a solid data migration strategy in place can help ensure a smooth transition to the new system without any loss of important data. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind when planning your data migration strategy.
The first step in any data migration strategy is to assess your current data. This involves identifying all the data that will need to be migrated to the new system, as well as determining the quality and accuracy of that data. It’s important to clean up any outdated or incorrect data before migrating it to the new system, as this can impact the functionality and effectiveness of the new ERP system.
Once you have assessed your data, the next step is to determine the best method for migrating it to the new system. There are several approaches to data migration, including manual data entry, data extraction and transformation through ETL processes, or using specialized migration tools. The best approach will depend on the volume and complexity of your data, as well as your budget and timeline constraints.
Another important consideration in your data migration strategy is ensuring data integrity and security. This involves setting up proper data validation processes to ensure that the data being migrated is accurate and complete. It’s also important to consider data encryption and other security measures to protect sensitive data during the migration process.
Testing is a crucial component of any data migration strategy. Before going live with the new ERP system, it’s essential to thoroughly test the data migration process to identify any issues or errors that may arise. This may involve running test migrations with sample data, as well as validating the migrated data to ensure its accuracy and completeness.
Lastly, it’s important to have a contingency plan in place in case any issues arise during the data migration process. This may include having backup systems in place to revert to in case of data loss, as well as having a team of experts on hand to troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
By taking the time to develop a solid data migration strategy, you can help ensure a successful ERP Go-Live that minimizes disruptions and maximizes the effectiveness of your new system. Don’t rush through this crucial step in the implementation process – proper planning and preparation will pay off in the long run.
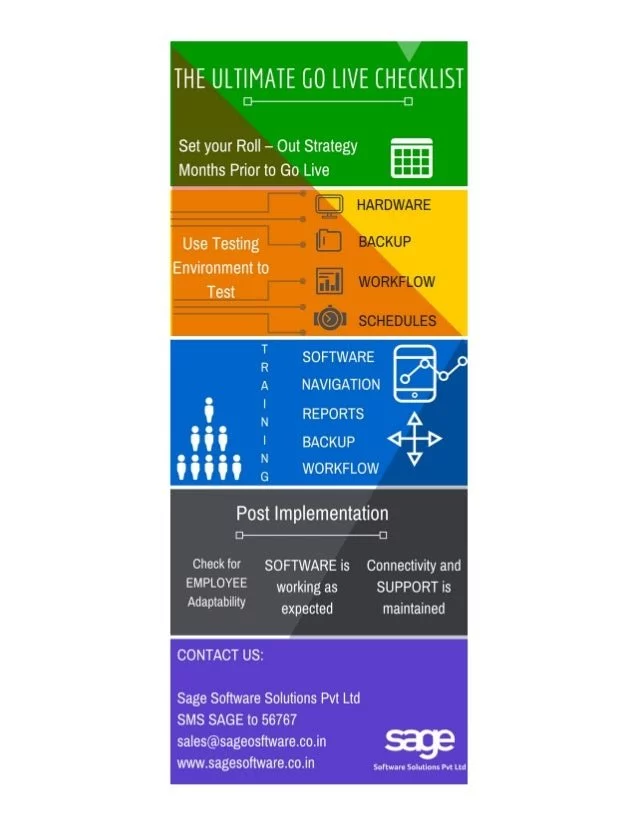
System Testing and Training
System Testing is a crucial phase in the ERP Go-Live Checklist that ensures the smooth functioning of the new system. This phase involves testing the various modules of the ERP system to identify any bugs, errors, or discrepancies. It is essential to conduct thorough testing to ensure that the system performs as expected and meets the business requirements.
During the System Testing phase, the project team should perform different types of tests, such as unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing. Unit testing involves testing individual modules or components of the system to ensure they work correctly. Integration testing, on the other hand, involves testing the interactions between different modules to ensure they work together seamlessly. User acceptance testing involves testing the system from an end-user perspective to ensure it meets their requirements and is easy to use.
It is essential to involve key stakeholders, end-users, and subject matter experts in the testing phase to ensure all aspects of the system are thoroughly tested. This will help identify any issues or discrepancies before the system goes live, allowing the project team to address them proactively.
Training is another critical aspect of the ERP Go-Live Checklist that is often overlooked. Ensuring that end-users are adequately trained on how to use the new system will help maximize the benefits of the ERP implementation. Training should be customized based on the roles and responsibilities of the end-users to ensure they understand how to perform their tasks using the new system.
Training sessions should be conducted before the system goes live to give end-users time to familiarize themselves with the new system and address any questions or concerns they may have. Providing training materials, such as user manuals, guides, and tutorials, can also help end-users navigate the system effectively and troubleshoot common issues on their own.
Additionally, it is essential to provide ongoing support and training to end-users even after the system has gone live. This will help them adapt to any changes or updates in the system and ensure they continue to use it effectively. Regular feedback sessions and refresher training can also help reinforce best practices and ensure end-users are maximizing the benefits of the new system.
In conclusion, System Testing and Training are essential components of the ERP Go-Live Checklist that play a crucial role in the successful implementation of a new ERP system. By conducting thorough testing and providing adequate training to end-users, organizations can ensure a smooth transition to the new system and maximize the benefits it offers.
Change Management Process
Implementing a new ERP system can be a daunting task for any organization. One of the key components of a successful ERP implementation is the change management process. Change management is the process of helping individuals and the organization transition from the current state to the desired future state. It involves planning, communicating, and managing changes effectively to ensure a smooth transition. Here are some key steps to take in the change management process:
1. Identify Stakeholders: The first step in the change management process is to identify all stakeholders who will be affected by the ERP implementation. This includes employees, managers, executives, and any other individuals who will be impacted by the change. It is important to involve key stakeholders early on in the process to gain their buy-in and support.
2. Communication Plan: A well-thought-out communication plan is essential in managing change effectively. The communication plan should outline how information will be shared, who will be responsible for communicating changes, and when updates will be provided. Communication should be clear, consistent, and timely to keep stakeholders informed throughout the ERP implementation process.
3. Training and Development: Providing adequate training and development opportunities for employees is crucial in helping them adapt to the new ERP system. Training sessions should be tailored to the specific needs of different user groups and delivered in a way that is easy to understand. Continuous support and ongoing training will help employees feel confident in using the new system.
4. Employee Engagement: Engaging employees in the change management process is key to ensuring a successful ERP implementation. Employees should be involved in decision-making, provided with opportunities to give feedback, and encouraged to participate in training and development activities. By involving employees in the process, organizations can build a sense of ownership and commitment to the new ERP system.
5. Monitoring and Evaluation: Throughout the ERP implementation process, it is important to monitor progress and evaluate the effectiveness of the change management process. Tracking key performance indicators, gathering feedback from stakeholders, and making adjustments as needed will help ensure a smooth transition to the new ERP system. Continuous monitoring and evaluation will also provide valuable insights for future change initiatives.
6. Celebrate Successes: Recognizing and celebrating small successes along the way can help boost morale and maintain momentum during the ERP implementation process. Whether it’s reaching a milestone, overcoming a challenge, or achieving a key objective, taking the time to acknowledge achievements will motivate employees and reinforce the benefits of the new ERP system.
By following these steps in the change management process, organizations can increase the likelihood of a successful ERP implementation. Effective change management is essential in helping employees transition to the new system smoothly, minimize resistance to change, and maximize the benefits of the ERP system for the organization as a whole.
Post Go-Live Support and Evaluation
Once your ERP system has been successfully implemented and gone live, it is crucial to provide post go-live support to ensure that the system continues to run smoothly and address any issues that may arise. This includes providing ongoing user training, troubleshooting technical issues, and maintaining system updates. Post go-live support is essential to ensure that your team is fully trained and comfortable using the new system and to address any unforeseen challenges that may arise.
One of the key aspects of post go-live support is providing ongoing training to users. Even after the initial training sessions during implementation, users may encounter new features or functionalities that they are not familiar with. Providing ongoing training sessions or resources can help users feel more comfortable and confident using the system, leading to increased adoption and efficiency.
In addition to training, it is important to have a dedicated support team in place to troubleshoot any technical issues that may arise post go-live. This team can work closely with users to identify and resolve any issues quickly, minimizing downtime and disruption to operations. Regularly scheduled check-ins with users can also help to proactively identify any potential issues before they escalate.
As part of post go-live support, it is also essential to regularly update and maintain the ERP system. This includes applying patches, updates, and fixes provided by the ERP vendor to ensure that the system is running smoothly and securely. Regular maintenance can help to prevent issues and improve system performance over time.
Furthermore, conducting post go-live evaluations can help to assess the success of the implementation and identify areas for improvement. Evaluations can include gathering feedback from users, analyzing system performance metrics, and assessing the overall impact of the ERP system on business operations. This information can be used to make informed decisions on future system enhancements or additional training needs.
In conclusion, post go-live support and evaluation are essential components of successful ERP implementation. By providing ongoing support to users, maintaining system updates, and conducting regular evaluations, organizations can ensure that their ERP system continues to meet their business needs and drives efficiency and growth.
Originally posted 2024-02-01 00:52:51.